HVAC SYSTEMS
At AMW Renewables, we specialize in smart HVAC solutions that help businesses maximize comfort, reduce energy costs, and contribute to sustainability goals. Our expert team will guide you in selecting and installing the perfect system, ensuring that you benefit from cutting-edge technology and optimal performance.
Smart HVAC systems are a future-forward solution that delivers both energy efficiency and a more comfortable living or working space.
Central HVAC Systems
- Forced Air Systems: Common in homes and larger buildings, forced air systems distribute heated or cooled air through a network of ducts and vents.
- Heat Pump Systems: Heat pumps transfer heat between indoor and outdoor spaces, providing both heating and cooling. They are energy-efficient, especially in moderate climates.
Hybrid HVAC Systems
Hybrid systems combine two types of energy sources, typically an electric heat pump and a gas furnace. The system switches between these two sources depending on the outdoor temperature and energy efficiency.
Geothermal HVAC Systems (Ground Source Heat Pumps)
Geothermal systems use the earth’s stable underground temperatures to heat and cool a building. A ground loop absorbs heat from the earth during the winter and disperses heat back into the ground during the summer.
Zoned HVAC Systems
Zoned systems divide a building into different areas or "zones," each with its own thermostat. A central HVAC unit then heats or cools specific zones based on the demand in each area, enhancing comfort and efficiency.


Interested in any of our renewable products? Get a FREE quote from our specialised team now.

Electric Boiler Upgrades
At AMW Renewables, we offer advanced electric boiler solutions that are highly efficient, easy to install, and environmentally friendly. Whether you're upgrading your heating system or looking for a reliable, low-maintenance option, our electric boilers are designed to meet your specific needs while helping you reduce your carbon footprint.
Electric boilers use resistive heating elements inside the unit to heat water. When electricity flows through the elements, they become hot, and this heat is transferred to the water circulating in the system.
Types of Electric Boilers we provide:
1. Electric Storage Boilers: These systems store hot water in a tank or cylinder, allowing for a consistent supply of hot water to be used throughout the day. They are suitable for l businesses.
2. Electric Flow Boilers: Similar to central heating boilers, these heat water and circulate it through radiators to provide space heating but may require a separate hot water cylinder for domestic hot water use.
Benefits of Electric Boilers:
- Energy Efficiency: Electric boilers convert nearly 100% of the electricity they consume into heat, making them very efficient compared to gas boilers that lose energy through combustion.
- Zero Emissions On-Site: Since they don’t burn fuel, electric boilers produce no carbon emissions during operation, making them an eco-friendly heating solution, especially when paired with renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
- Compact and Easy to Install: Electric boilers are generally smaller and easier to install than traditional boilers, as they don’t require a flue or gas connection.
- Low Maintenance: Electric boilers have fewer moving parts than traditional boilers, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and lowering overall running costs.
Interested in any of our renewable products? Get a FREE quote from our specialised team now.


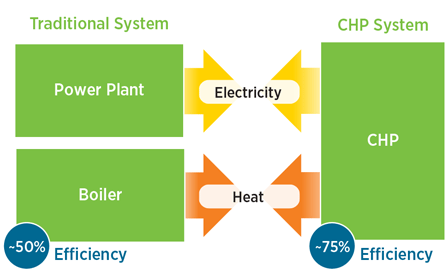
Combined Heat and Power Systems
Combined Heat and Power (CHP), also known as cogeneration, is a highly efficient system that generates both electricity and useful heat from a single energy source, typically natural gas, biomass, or other fuels. CHP systems are commonly used in commercial, industrial, and residential settings to increase energy efficiency and reduce overall energy costs.
How CHP Systems Operate:
Energy Source: CHP systems use a fuel source (such as natural gas, biomass, or renewable fuels) to power an engine, turbine, or other prime mover that generates electricity.
Electricity Generation: The process of electricity generation produces heat as a by-product. In traditional power plants, this excess heat is often wasted. However, in a CHP system, this heat is captured and repurposed.
Heat Recovery: The heat generated during electricity production is recovered and used to provide heating or hot water for buildings, industrial processes, or district heating networks.
Key Benefits of Combined Heat and Power:
Increased Efficiency: CHP systems can achieve efficiency rates of up to 80-90%, far higher than traditional power plants that only achieve about 30-40% efficiency. By utilizing both electricity and heat, CHP systems reduce fuel waste.
Cost Savings: By generating both electricity and heat on-site, businesses and homes reduce the need to purchase power from the grid and separate heating fuel, leading to significant savings on energy bills.
Lower Carbon Emissions: CHP systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using fuel more efficiently. This results in a lower carbon footprint, contributing to sustainability and environmental goals.
Energy Independence: CHP systems provide on-site electricity and heat generation, reducing reliance on external energy suppliers and providing energy security, especially during power outages.
Versatility: CHP systems can run on a variety of fuels, including natural gas, biomass, and even renewable energy sources like biogas, allowing for flexibility in fuel choice and energy supply.
Resilience: CHP systems can operate independently of the grid, providing backup power during outages and ensuring continuous heating and electricity supply, particularly important for critical infrastructure like hospitals, data centres, and factories.
Applications of CHP Systems:
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and manufacturing plants benefit from CHP by using the waste heat for process heating, space heating, or cooling, significantly improving efficiency.
- Commercial Buildings: Hotels, office buildings, and shopping centres can use CHP for heating, cooling, and electricity, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- District Heating: CHP systems are often used in district heating networks, where the waste heat from electricity generation is distributed to multiple buildings in urban areas for space heating and hot water.
- Hospitals & Data Centres: These facilities require continuous, reliable energy. CHP systems provide resilience and energy security while reducing costs.
Our Accreditations

We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.

